-
41
-
2025-08-28 16:58:26
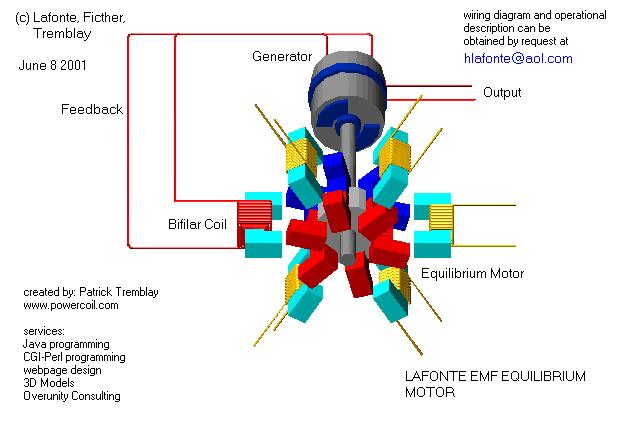
1. Permanent magnet motor: An electric motor that uses permanent magnets to provide a magnetic field. For an electric motor to produce work, two conditions are required: the presence of a magnetic field and the flow of current within the field.
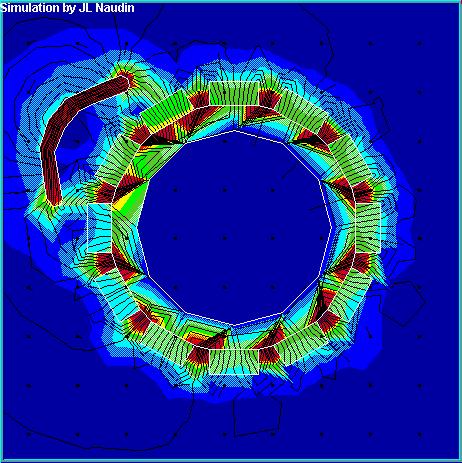
2. DC Motor: This motor converts DC electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is widely used in electric traction due to its excellent speed regulation. The excitation method of a DC motor refers to how the excitation winding is powered to generate the excitation magnetomotive force and establish the main magnetic field.
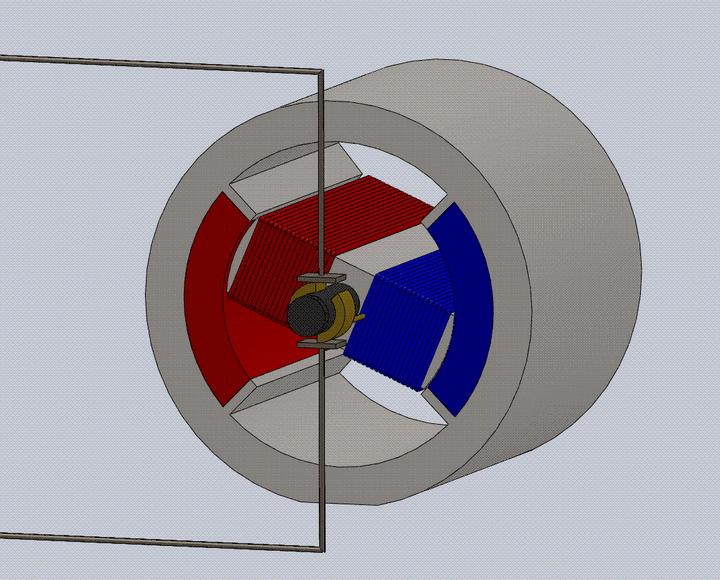
3. AC motor: A machine used to convert mechanical energy into AC electrical energy. AC motors lack a commutator and are simpler in structure than DC motors. They are easier to manufacture, more robust, and can easily be made into high-speed, high-voltage, high-current, and high-capacity motors.
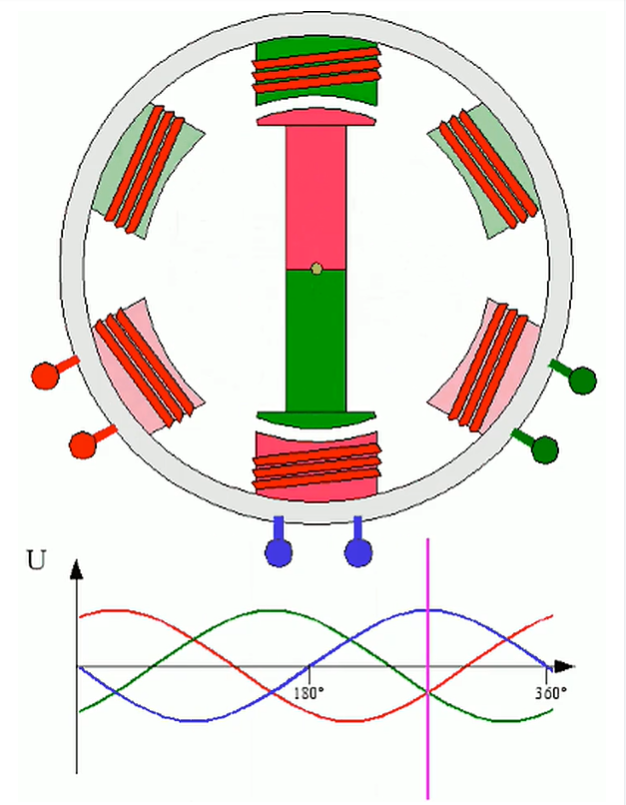
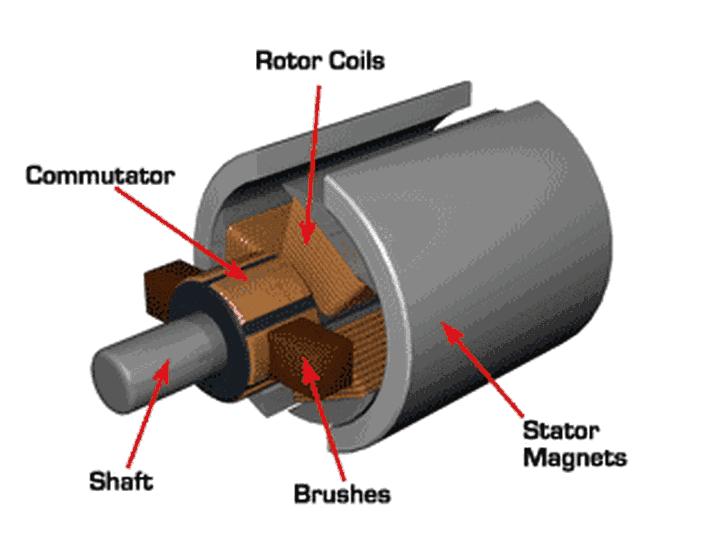
4. Permanent Magnet DC Motor: This motor consists of a stator, rotor, commutator (also known as a rectifier), and brushes. The stator generates a magnetic field. The rotor rotates under the action of the stator's magnetic field, generating torque. The commutator changes the direction of the current, allowing the rotor to rotate continuously. In other words, a DC voltage is applied to the brushes, which is then fed to the rotor coils via the commutator. This current flows through the brushes, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the stator's fixed magnetic field, forcing the rotor to rotate. As it rotates, the interaction of the magnetic fields generates a back electromotive force (EMF). Its magnitude is proportional to the rotor speed and its direction is opposite to the applied DC voltage.
5. Quantum magneto: A generator that produces high-voltage periodic pulses (rather than continuous current). A generator (or magneto) utilizes the reverse process of electromagnetic conversion. An electromagnet typically consists of an iron core (armature) surrounded by a coil of wire. When you apply current to the electromagnet coil, the coil generates a magnetic field in the armature.
6. Single-phase induction motor: also known as single-phase asynchronous motor, it is an AC motor that converts electromechanical energy into mechanical energy by the interaction between the rotating magnetic field of the air gap and the induced current of the rotor winding to generate electromagnetic torque. It is used in power applications with only single-phase power supply to drive small machines such as small crushers, grinding machines, etc., with a general power of less than 1500W.
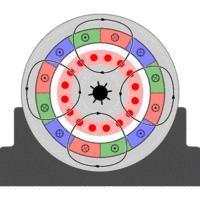
7. Three-phase induction motor: An AC motor that generates electromagnetic torque by the interaction between the rotating magnetic field formed by the stator winding and the magnetic field of the induced current in the rotor winding. It is a type of induction motor.
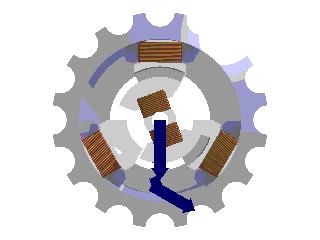
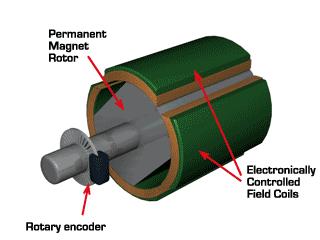
8. Brushless DC Motor: The stator (the stationary part) of the motor is composed of coils, or windings. The rotor (the rotating part) is a permanent magnet. A microcontroller controls the flow of current to each coil based on the rotor's position, causing the magnetic field generated by the coils to change, thereby constantly pulling the rotor forward and causing it to rotate. This is the operating principle of a brushless DC motor.
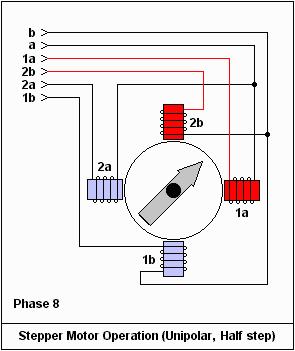
9. Stepper motor: An open-loop control element that converts electrical pulse signals into angular or linear displacement. Its operating principle is to use electronic circuits to convert DC power into a time-sharing, multi-phase timing-controlled current. This current powers the stepper motor, enabling it to operate properly. The driver provides time-sharing power to the stepper motor, a multi-phase timing controller.
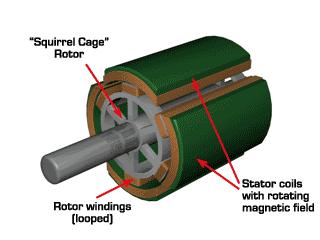
10. Squirrel cage motor: A three-phase asynchronous motor whose rotor winding is not made of insulated wire, but is welded or cast with aluminum or copper bars and short-circuit rings.
11. Balanced motor